11 KiB
Usage
Start Parameters
pykms_Server.py
Follows a list of usable parameters:
ip <IPADDRESS>
Instructs py-kms to listen on IPADDRESS (can be an hostname too). If this option is not specified, IPADDRESS 0.0.0.0 is used.
port <PORT>
Define TCP PORT the KMS service is listening on. Default is 1688.
-e or --epid <EPID>
Enhanced Privacy ID (EPID) is a cryptographic scheme for providing anonymous signatures. Use EPID as Windows EPID. If no EPID is specified, a random one will be generated.
-l or --lcid <LCID>
Do not randomize the locale ID part of the EPID and use LCID instead. The Language Code Identifier (LCID) describes localizable information in Windows. This structure is used to identify specific languages for the purpose of customizing software for particular languages and cultures. For example, it can specify the way dates, times, and numbers are formatted as strings. It can also specify paper sizes and preferred sort order based on language elements. The LCID must be specified as a decimal number (example: 1049 for "Russian - Russia"). By default py-kms generates a valid locale ID but this may lead to a value which is unlikely to occur in your country. You may want to select the locale ID of your country instead. See here for a list of valid LCIDs. If an EPID is manually specified, this setting is ignored. Default is a fixed LCID of 1033 (English - US).
-w or --hwid <HWID>
Use specified HWID for all products. Hardware Identification is a security measure used by Microsoft upon the activation of the Windows operating system. As part of the Product Activation system, a unique HWID number is generated when the operating system is first installed. The HWID identifies the hardware components that the system is utilizing, and this number is communicated to Microsoft. Every 10 days and at every reboot the operating system will generate another HWID number and compare it to the original to make sure that the operating system is still running on the same device. If the two HWID numbers differ too much then the operating system will shut down until Microsoft reactivates the product. The theory behind HWID is to ensure that the operating system is not being used on any device other than the one for which it was purchased and registered. HWID must be an 16-character string of hex characters that are interpreted as a series of 8 bytes (big endian). Default is 364F463A8863D35F. To auto generate the HWID, type
-w RANDOM.
-c or --client-count <CLIENTCOUNT>
Use this flag to specify the current CLIENTCOUNT. Default is None. Remember that a number >=25 is required to enable activation of client OSes while for server OSes and Office >=5.
-a or --activation-interval <ACTIVATIONINTERVAL>
Instructs clients to retry activation every ACTIVATIONINTERVAL minutes if it was unsuccessful, e.g. because it could not reach the server. The default is 120 minutes (2 hours).
-r or --renewal-interval <RENEWALINTERVAL>
Instructs clients to renew activation every RENEWALINTERVAL minutes. The default is 10080 minutes (7 days).
-s or --sqlite
Use this option to store request information from unique clients in an SQLite database. Deactivated by default. If enabled the default database file is pykms_database.db. You can also provide a specific location.
-t0 or --timeout-idle <TIMEOUT>
Maximum inactivity time (in seconds) after which the connection with the client is closed. Default setting is serve forever (no timeout).
-y or --async-msg
With high levels of logging (e.g hundreds of log statements), in a traditional synchronous log model, the overhead involved becomes more expensive, so using this option you enable printing (pretty / logging) messages asynchronously reducing time-consuming. Deactivated by default.
-V or --loglevel <{CRITICAL, ERROR, WARNING, INFO, DEBUG, MININFO}>
Use this flag to set a logging loglevel. The default is ERROR. example:
user@host ~/path/to/folder/py-kms $ python3 pykms_Server.py -V INFO
creates pykms_logserver.log with these initial messages:
Mon, 12 Jun 2017 22:09:00 INFO TCP server listening at 0.0.0.0 on port 1688.
Mon, 12 Jun 2017 22:09:00 INFO HWID: 364F463A8863D35F
-F or --logfile <LOGFILE>
Creates a LOGFILE.log logging file. The default is named pykms_logserver.log. example:
user@host ~/path/to/folder/py-kms $ python3 pykms_Server.py 192.168.1.102 8080 -F ~/path/to/folder/py-kms/newlogfile.log -V INFO -w RANDOM
creates newlogfile.log with these initial messages:
Mon, 12 Jun 2017 22:09:00 INFO TCP server listening at 192.168.1.102 on port 8080.
Mon, 12 Jun 2017 22:09:00 INFO HWID: 58C4F4E53AE14224
You can also enable other suboptions of -F doing what is reported in the following table:
| command | pretty msg | logging msg | logfile |
|---|---|---|---|
-F <logfile> |
ON | OFF | ON |
-F STDOUT |
OFF | ON | OFF |
-F FILESTDOUT <logfile> |
OFF | ON | ON |
-F STDOUTOFF <logfile> |
OFF | OFF | ON |
-F FILEOFF |
ON | OFF | OFF |
-S or --logsize <MAXSIZE>
Use this flag to set a maximum size (in MB) to the output log file. Deactivated by default.
pykms_Client.py
If py-kms server doesn't works correctly, you can test it with the KMS client pykms_Client.py, running on the same machine where you started pykms_Server.py.
For example (in separated bash windows) run these commands:
user@host ~/path/to/folder/py-kms $ python3 pykms_Server.py -V DEBUG
user@host ~/path/to/folder/py-kms $ python3 pykms_Client.py -V DEBUG
Or if you want better specify:
user@host ~/path/to/folder/py-kms $ python3 pykms_Server.py <YOUR_IPADDRESS> 1688 -V DEBUG
user@host ~/path/to/folder/py-kms $ python3 pykms_Client.py <YOUR_IPADDRESS> 1688 -V DEBUG
You can also put further parameters as defined below:
ip <IPADDRESS>
Define IPADDRESS (or hostname) of py-kms' KMS Server. This parameter is always required.
port <PORT>
Define TCP PORT the KMS service is listening on. Default is 1688.
-m or --mode <{WindowsVista, Windows7, Windows8, Windows8.1, Windows10, Office2010, Office2013, Office2016, Office2019}>
Use this flag to manually specify a Microsoft PRODUCTNAME for testing the KMS server. Default is Windows8.1.
-c or --cmid <CMID>
Use this flag to manually specify a CMID to use. If no CMID is specified, a random one will be generated. The Microsoft KMS host machine identifies KMS clients with a unique Client Machine ID (CMID, example: ae3a27d1-b73a-4734-9878-70c949815218). For a KMS client to successfully activate, the KMS server needs to meet a threshold, which is a minimum count for KMS clients. Once a KMS server records a count which meets or exceeds threshold, KMS clients will begin to activate successfully. Each unique CMID recorded by KMS server adds towards the count threshold for KMS clients. This are retained by the KMS server for a maximum of 30 days after the last activation request with that CMID. Note that duplicate CMID only impacts on KMS server machine count of client machines. Once KMS server meets minimum threshold, KMS clients will activate regardless of CMID being unique for a subset of specific machines or not.
-n or --name <MACHINENAME>
Use this flag to manually specify an ASCII MACHINENAME to use. If no MACHINENAME is specified a random one will be generated.
-y or --async-msg
Prints pretty / logging messages asynchronously. Deactivated by default.
-V or --loglevel <{CRITICAL, ERROR, WARNING, INFO, DEBUG, MININFO}>
Use this flag to set a logging loglevel. The default is ERROR.
-F or --logfile <LOGFILE>
Creates a LOGFILE.log logging file. The default is named pykms_logclient.log. You can enable same pykms_Server.py suboptions of
-F.
-S or --logsize <MAXSIZE>
Use this flag to set a maximum size (in MB) to the output log file. Deactivated by default.
Activation Procedure
The product asks for a key during installation, so it needs you to enter the GVLK. Then the user can set connection parameters, while KMS server must already be running on server machine. Finally with specific commands, activation occurs automatically and can be extended later every time for another 180 (or 30 or 45) days.
Windows
The //nologo option of cscript was used only to hide the startup logo.
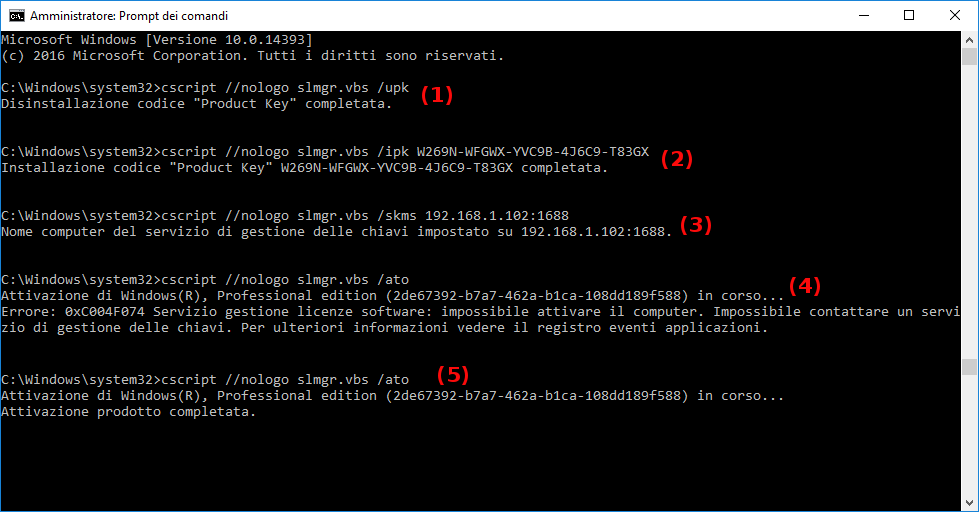
- Run a Command Prompt as Administrator (you are directly in
C:\Windows\System32path). - This is optional, it's for unistalling any existing product key.
- Then put in your product's GVLK.
- Set connection parameters.
- Try online activation, but... if that fails with error
0xC004F074you’ll most likely have to configure your firewall that it accepts incoming connections on TCP port 1688. So for Linux users (server-side withpykms_Server.pyrunning):sudo ufw allow 1688(to remove this rulesudo ufw delete allow 1688) - Attempt online activation (now with traffic on 1688 enabled).
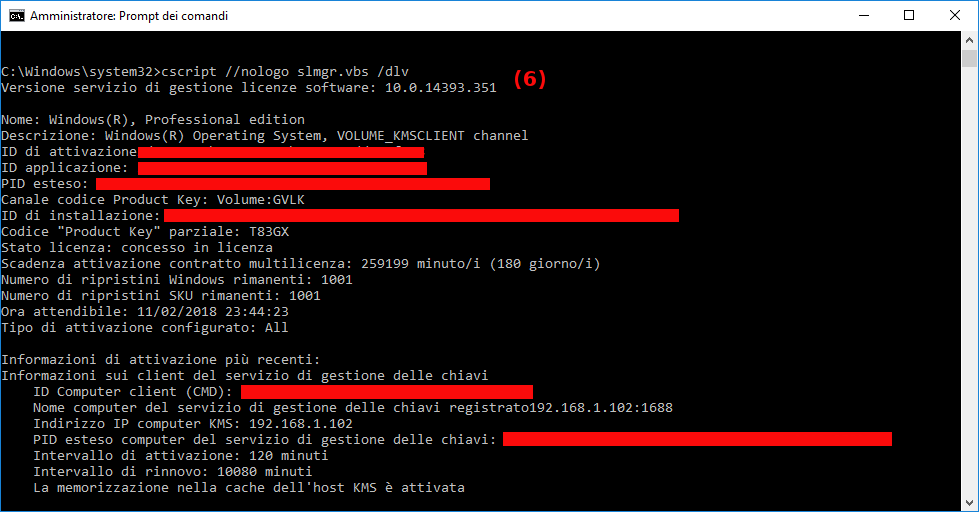
- View license informations (optional).
Office
Note that you’ll have to install a volume license (VL) version of Office. Office versions downloaded from MSDN and / or Technet are non-VL.
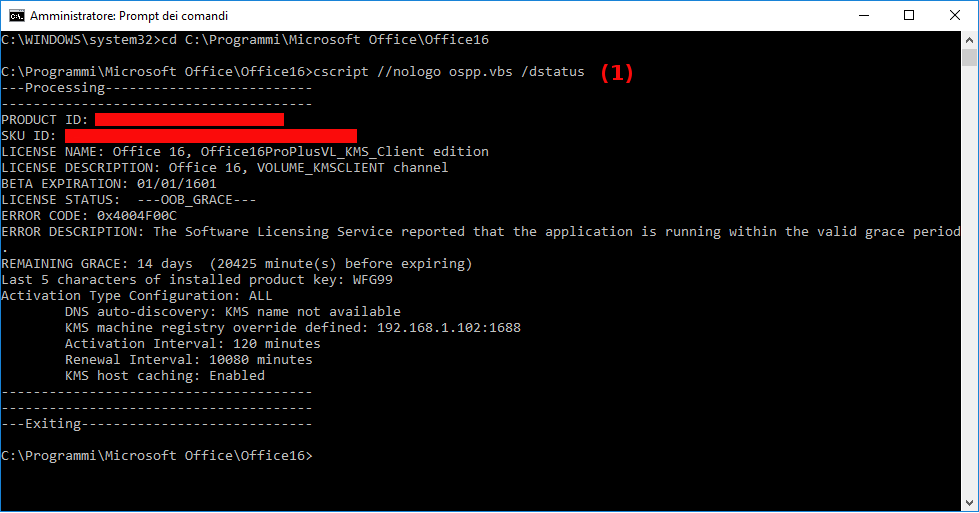
- Run a Command Prompt as Administrator and navigate to Office folder
cd C:\ProgramFiles\Microsoft Office\OfficeXX(64-bit path) orcd C:\ProgramFiles(x86)\Microsoft Office\OfficeXX(32-bit path), where XX =14for Office 2010,15for Office 2013,16for Office 2016 or Office 2019. - As you can see, running
/dstatus, my Office is expiring (14 days remaining). - Only for example, let's go to uninstall this product.
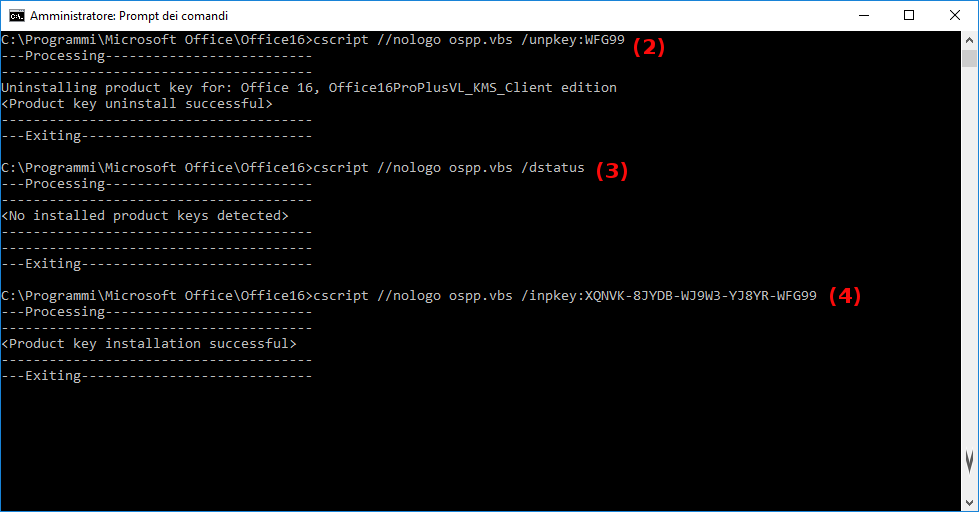
- This is confirmed running
/dstatusagain. - Now i put my product's GVLK (and you your key).
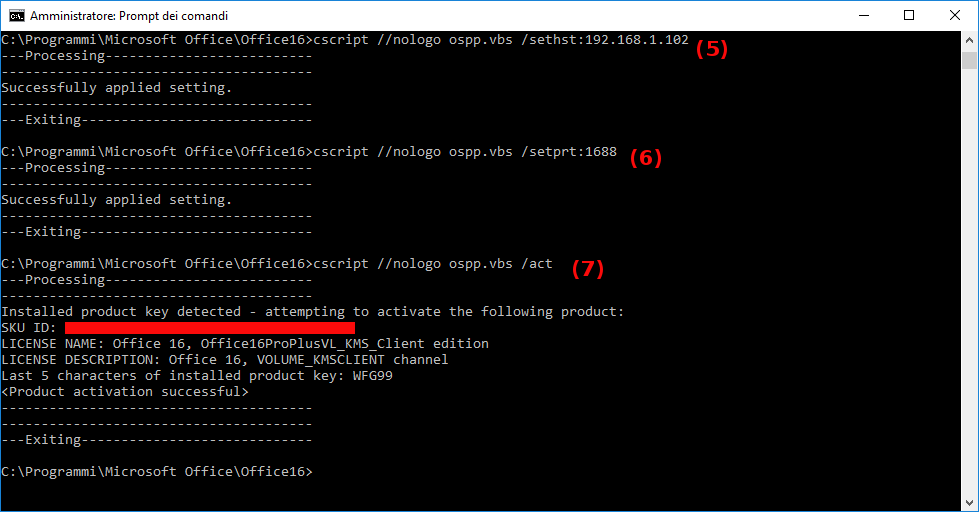
- Set the connection parameter KMS server address.
- Set the connection parameter KMS server port.
- Activate installed Office product key.
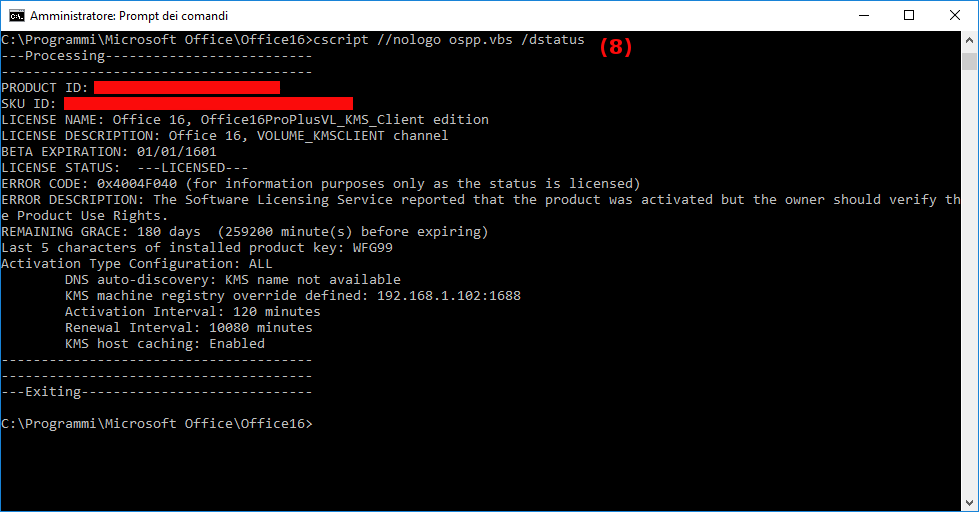
- View license informations (in my case product is now licensed and remaining grace 180 days as expected).
Supported Products
Note that it is possible to activate all versions in the VL (Volume License) channel, so long as you provide the proper key to let Windows know that it should be activating against a KMS server. KMS activation can't be used for Retail channel products, however you can install a VL product key specific to your edition of Windows even if it was installed as Retail. This effectively converts Retail installation to VL channel and will allow you to activate from a KMS server. However, this is not valid for Office's products, so Office, Project and Visio must be always volume license versions. Newer version may work as long as the KMS protocol does not change...